Understanding Hook worm Dogs: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
This disease affects dogs commonly and with the spread of these parasitic worms, a dog may suffer a lot of health complications. These are very small worms that can infect dogs regardless of breed and age and cause from quite mild discomfort to fatal anemia. To the pet owners out there, it is very important to learn all about hook worm Dogs to keep your furry friends in good health and happiness. In the following guide, we will look at the signs that your dog may have hookworms, how the worms can be treated, and how their spread can be prevented.
What Are Hookworms?
Hookworms are more or less slim, thread-like worms that can be found in the duodenum and jejunum of dogs. They anchor themselves to the liner of the intestinal tract and feed on the blood of the host causing different diseases. The most common species of hookworms that infect dogs include:
Ancylostoma caninum
This is the most common and invasive kind seen in dogs that can cause profuse bleeding and anemia.
Ancylostoma braziliense
Although it might not be as dangerous as A. caninum, this species poses a great risk, especially to individuals living in tropical and subtropical climates.
Uncinaria Stenocephala
Common in colder regions, this species is relatively less virulent than A. caninum.
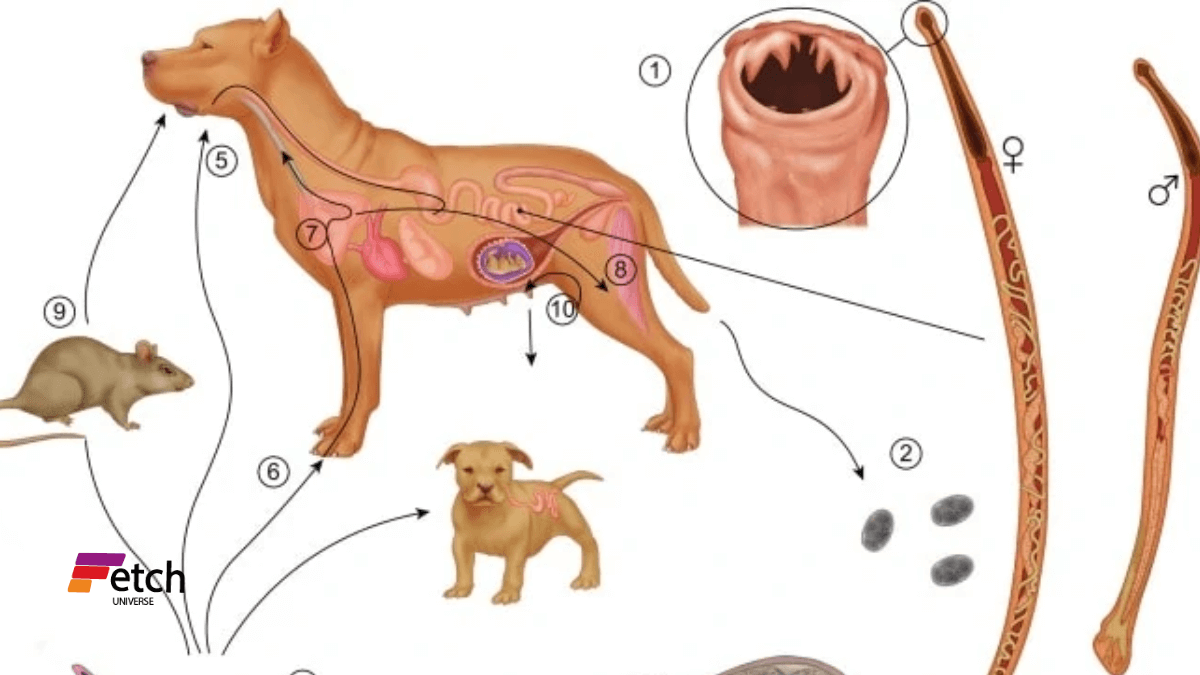
How Dogs Get Hookworms
Transmission Methods
Hookworms can infect dogs through several routes:
Ingestion of Infective Larvae: Hookworms may be swallowed directly by dogs through contaminated soil, water, and feces.
Skin Penetration: The larvae can directly burrow into the skin of the dog mostly in the paws or belly if the dog lays on the affected ground.
Transplacental or Transmammary Transmission: A puppy can be born with hookworms coming from the mother or even through the milk.
Risk Factors
Foods that are risky for human beings are also bad for puppies since their immune systems are still developing. Furthermore, dogs are associated with dusty environments, and outdoor and unsanitary environments are more prone to infections.
Symptoms of Hook worms Dogs
The signs of hookworm infection can be dependent on the level of the parasite infestation and the age of the dog. Puppies and immunocompromised dogs should be expected to show worse signs than ordinary healthy dogs.
Early Symptoms
- Lethargy and Fatigue
- Loss of Appetite
- Weight Loss
Advanced Symptoms
Anemia: Hookworms are blood suckers and if my baby was infected, his gums would probably have gone pale and he would probably be weak.
Diarrhea: May become dark and tarry as it’s an indication of blood loss.
Abdominal Pain: This may cause some discomfort or condition known as bloating in dogs.
Symptoms in Puppies
Stunted Growth
Severe Anemia
Difficulty Breathing
Diagnosing Hookworms in Dogs
Veterinary Examination
In diagnosing a hookworm infestation in dogs, a veterinarian will examine the dog and discuss his or her medical history.
Fecal Testing
Microscopic Examination: In fact, an accurate diagnosis of hookworm infection is by assessing the eggs within the fecal floatation.
Repeat Testing: It might take several tests to establish the presence of hookworms.

Treatment for Hookworms in Dogs
The medical management of hookworms is easy and if detected at the right time, the results are usually favorable. It includes drug treatment and measures to relieve symptoms.
Anthelmintic Medications
Common Dewormers: Fenbendazole, pyrantel phosphoromat, and milbemycin oxime are some drugs, which help in eradicating hookworms.
Dosage and Duration: Therefore, it is crucial to use the doctor’s instructions to achieve a complete removal of the parasite.
Supportive Care
Iron Supplements: In anemia resulting from blood loss, to replenish the body’s red blood cell supply.
Nutritional Support: Hong-rich diets may help with recovery.
Fluid Therapy: As a matter of importance especially for dogs that experience severe cases of dehydration and those that suffer from anemia.
Follow-Up Care
Therefore, to confirm whether hookworms have been fully eradicated, stool samples ought to be retried for tests after treatment.
Complications of Untreated Hookworms
If left untreated, hookworms can lead to severe health complications, including:
Chronic Anemia: Chronic bleeding can cause general debilitation and exacerbation of further illnesses in the dog.
Intestinal Damage: They said that long-term infestations can culminate in inflammation and scarring within the intestines.
Infections: These wounds from larvae penetration may become septic.
Preventing Hook worms Dogs
All efforts have to be made to prevent the disease in canine since this affects them. Here are key steps to reduce the risk:
Regular Deworming
Administer Deworming Medications: It is recommended that you adhere to your vet’s advice on deworming your pets.
Treat Puppies: Puppies should undergo deworming at the age of 02, 04, 06 and 08 weeks.
Maintaining Hygiene
Clean Living Environment: Wash or replace your dog’s bedding and the areas where it spends most of its time often.
Proper Waste Disposal: Quickly clear and dispose of dog droppings to reduce pollution influences.
Avoid High-Risk Areas
Restrict dogs from accessing areas that he knows are always dirty with feces.
Wear shoes when taking dogs for a walk in uncharted or dirty territories.
Routine Veterinary Checkups
Visit your vet frequently to check your dog’s health and be sure to have the annual fecal test done.
Hookworms and Zoonotic Risks
It may also infect human host With hook worm Dogs forming a part of the intestinal parasites. Some of the larvae can directly burrow through the human skin leading to a disease characterized as cutaneous larva migrans. To protect yourself and your family:
Practice Good Hygiene
Wash Hands Thoroughly: Copied After coming into contact with the soil, pets, or feces.
Wear Gloves: Whenever you are gardening or tidying up after your dog.
Educate Your Family
Educate the children on the benefits of washing their hands and avoiding areas with the feces of the animals.
Hookworm in Multiple-Dog Households
In households with multiple dogs, managing a hookworm outbreak requires coordinated efforts:
Isolate Infected Dogs
Quarantine infected dogs since they can spread larvae, and wash contaminated areas.
Treat All Dogs Simultaneously
This means all asymptomatic dogs should also be treated to avoid having potential carriers.
Environmental Decontamination
Some of the appropriate disinfect to use include: To clean the kennels, yards, and other areas that the dogs often visit, the following disinfectants should be used.
The Importance of Early Intervention
If hookworm infestation is diagnosed and treated in the early stages, there will be no severe health consequences. Preventive care along with routine check-ups are important for your dog and can protect him or her from parasites.
Key Takeaways
Some signs that you should be watching for in your sick or ailing dog include; loss of appetite, lack of energy, and pale stomach lining.
Give your pet wormers as advised by your veterinarian.
To help ensure that you do not become reinfected with the virus, keep your living space clean.
Conclusion
This infectious organism is common in dogs and every owner needs to have basic knowledge about it. Still, as those who looked at the parasites that can be found in a dog, they are quite small but their influence can be rather large. If you identify the signs of hook worm Dogs infection early, treat it as soon as possible, and prevent it, you will shield your pet from the risks associated with it. Close monitoring by a veterinarian and cleanliness are between your dog’s paws’ most valuable friends.
Must Read:
Hellstar Hoodie: Wearing Talk of the Town as a Sign of Courage








